Sitka Spruce (Picea sitchensis)

Picea sitchensis, commonly known as Sitka Spruce, is a remarkable native species that plays a vital role in Pacific Northwest ecosystems. This hardy and adaptable plant has evolved specifically to thrive in the unique climate conditions of the region, making it an excellent choice for native landscaping and ecological restoration projects.
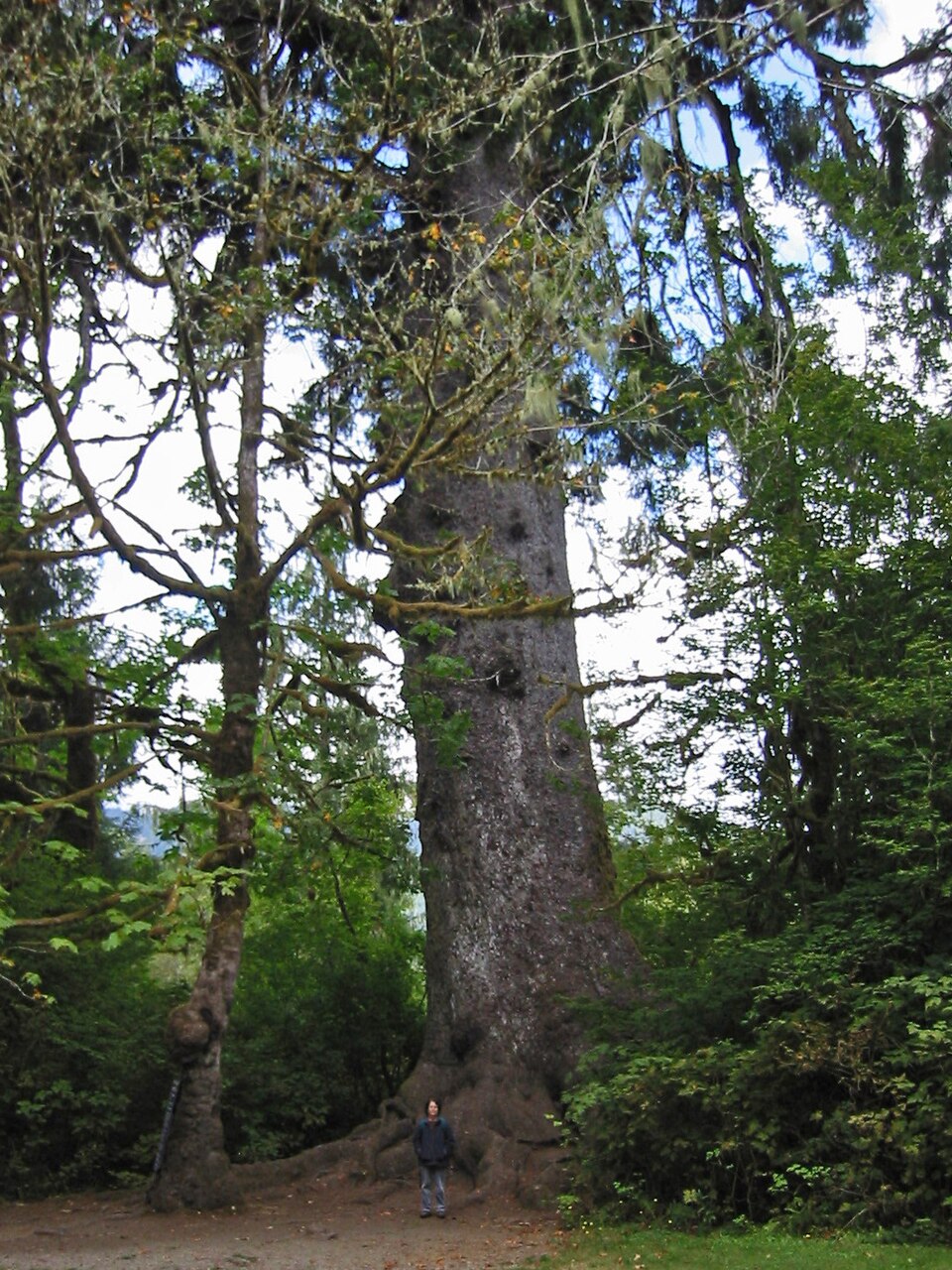
Giant Sitka Spruce Tree (Picea sitchensis)
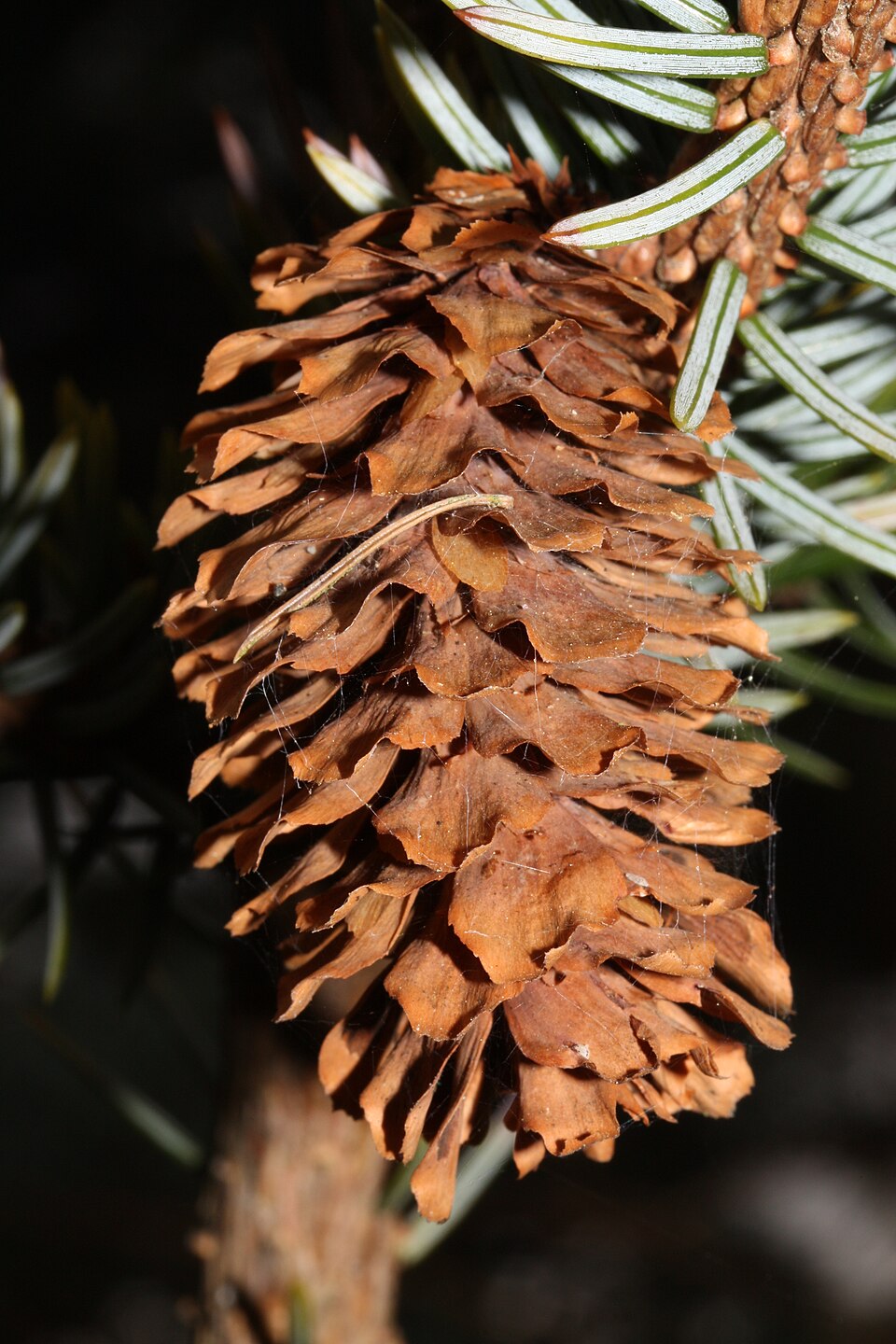

Sitka Spruce Cones (Picea sitchensis)
Quick Facts
| Scientific Name | Picea sitchensis |
| Plant Type | Native Plant |
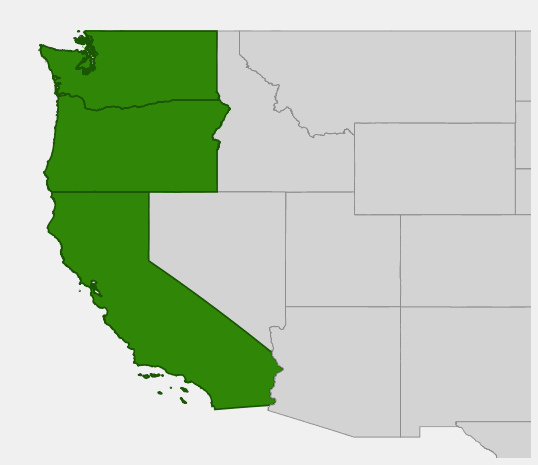
| Native Range | OR, WA, CA, AK |
| Sun Exposure | Varies by species |
| Water Needs | Moderate |
| Soil Type | Well-draining native soils |
| USDA Hardiness Zones | 6-9 |
Identification and Description
Sitka Spruce is a distinctive native species that can be identified by several key characteristics. Understanding these identification features helps both gardeners and naturalists recognize this valuable plant in the wild and distinguish it from similar species that may be found in the same habitat.
The overall form and growth pattern of Sitka Spruce reflects its evolutionary adaptation to Pacific Northwest conditions. Like many native species in this region, it has developed specific traits that allow it to thrive in the cool, moist winters and relatively dry summers that characterize much of its native range.
Native Range and Habitat
Sitka Spruce occurs naturally across a significant portion of the Pacific Northwest, with populations documented in OR, WA, CA, AK. This distribution pattern reflects the species’ specific habitat requirements and its role within the broader ecosystem.
Within its native range, Sitka Spruce typically establishes in habitats that provide the specific environmental conditions it requires for optimal growth and reproduction. These habitat preferences have evolved over thousands of years and represent the species’ ecological niche within Pacific Northwest ecosystems.
📋 Regional plant lists featuring Sitka Spruce: Western Oregon & Western Washington
Growing and Care Guide
Successfully cultivating Sitka Spruce requires understanding its natural habitat preferences and providing growing conditions that closely mimic those found in its native environment. This species has evolved specific adaptations to Pacific Northwest conditions, making it well-suited for regional gardens when properly sited and maintained.
Advanced growing tips for Sitka Spruce include understanding its natural growth patterns, seasonal care requirements, and long-term maintenance needs. Successful cultivation often depends on mimicking the plant’s native habitat conditions as closely as possible in the garden setting.
Site Selection and Preparation
Choosing the right location is crucial for successful establishment of Sitka Spruce. The ideal site should provide environmental conditions that closely match those found in the species’ natural habitat, including appropriate light levels, soil conditions, and moisture availability.
Site preparation should focus on creating growing conditions that support the plant’s natural growth patterns while ensuring long-term sustainability. This often involves soil amendments, drainage considerations, and planning for the plant’s mature size and growth habit.
Planting and Establishment
Proper planting technique is essential for successful establishment of Sitka Spruce. The best planting times typically coincide with the Pacific Northwest’s natural growing seasons, when temperatures and moisture levels are optimal for root development and early growth.
During the establishment period, regular monitoring and appropriate care help ensure the plant develops a strong root system and adapts well to its new environment. This critical phase often determines the long-term success of the planting.
Ongoing Maintenance
Once established, Sitka Spruce typically requires minimal maintenance when properly sited. However, some periodic care may be beneficial to maintain plant health and appearance, particularly in garden settings where growing conditions may differ from natural habitats.
Understanding the plant’s natural growth cycles and seasonal requirements helps gardeners provide appropriate care while avoiding unnecessary interventions that might disrupt the plant’s natural processes.
Cultural & Historical Uses
Sitka Spruce has been used by Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest for generations. Traditional uses include medicinal applications, food sources, and materials for tools and crafts. Many native plants like Sitka Spruce continue to play important roles in Indigenous cultural practices today.
Early European settlers and modern communities have also found uses for Sitka Spruce, both for practical applications and as ornamental plants in gardens and landscaping. The species contributes to local ecosystems and continues to be valued for restoration projects and wildlife habitat enhancement.
Today, Sitka Spruce is primarily appreciated for its ecological value and ornamental qualities in native plant gardens. Its role in supporting local wildlife populations makes it an important species for conservation and habitat restoration efforts throughout its range.
Wildlife and Ecological Value
Sitka Spruce serves important ecological functions within its native ecosystem, supporting biodiversity and providing habitat and food resources for various wildlife species. These ecological relationships have evolved over thousands of years and represent complex interdependencies between the plant and other organisms.
Wildlife Habitat and Food Sources
Many wildlife species depend on Sitka Spruce for critical resources including food, shelter, and nesting sites. These relationships often involve complex seasonal patterns that align with the plant’s growth cycles and resource availability.
Different parts of the plant may serve different ecological functions, with flowers, fruits, seeds, foliage, and even the overall plant structure providing resources for different wildlife communities throughout the year.
Ecosystem Services
Beyond its direct value to wildlife, Sitka Spruce contributes to broader ecosystem health through various ecological services. These may include soil stabilization, water cycle regulation, carbon sequestration, and support for beneficial insects and other organisms.
The species also plays important roles in plant community dynamics, influencing the establishment and success of other native species through various ecological interactions and environmental modifications.
Conservation and Restoration Value
Sitka Spruce represents an important component of Pacific Northwest biodiversity and plays valuable roles in habitat restoration and conservation projects. Its use in restoration efforts helps reestablish authentic native plant communities and support regional ecosystem health.
Conservation efforts for this species contribute to maintaining the genetic diversity and ecological integrity of Pacific Northwest ecosystems. These efforts are particularly important given ongoing habitat loss and environmental changes affecting the region.
Landscape Applications
In landscape settings, Sitka Spruce offers numerous benefits for gardeners seeking to create authentic Pacific Northwest gardens that support native biodiversity. Its natural beauty and ecological value make it an excellent choice for various landscape applications.
Successful landscape use requires understanding the plant’s natural requirements and growth patterns, allowing designers and gardeners to integrate it effectively into broader planting schemes that benefit both aesthetics and ecological function.
Design Considerations
When incorporating Sitka Spruce into landscape designs, consider its mature size, growth habit, seasonal changes, and relationships with other plants. These factors help ensure successful integration and long-term satisfaction with the planting.
The species works well in various design contexts, from naturalistic plantings that mimic wild habitats to more formal garden settings where native plants are featured prominently. Understanding its aesthetic qualities helps maximize its landscape impact.
Companion Planting
Sitka Spruce associates naturally with other Pacific Northwest native species, and these relationships can be replicated in garden settings to create authentic and ecologically functional plantings.
Choosing appropriate companion plants helps create plant communities that support each other through complementary resource use, beneficial interactions, and shared habitat requirements. These associations often result in more resilient and self-sustaining plantings.
Seasonal Interest and Maintenance
Throughout the year, Sitka Spruce provides various forms of interest and beauty, with seasonal changes that reflect its adaptation to Pacific Northwest climate patterns. Understanding these seasonal rhythms helps gardeners appreciate and care for the plant appropriately.
Different seasons may require different maintenance approaches, from supporting active growth during favorable conditions to protecting the plant during challenging periods. Aligning maintenance activities with natural cycles promotes plant health and reduces unnecessary interventions.
Frequently Asked Questions
How fast does Sitka Spruce grow?
Growth rate varies by species and growing conditions. Most native plants have moderate growth rates of 1-2 feet per year once established.
Is Sitka Spruce deer resistant?
Native plants vary in deer resistance. Check the Quick Facts table above for specific deer resistance information for this species.
When is the best time to plant Sitka Spruce?
Plant in fall or early spring for best establishment. Fall planting allows roots to develop over winter before summer stress.
Where can I buy Sitka Spruce?
Check our native plant nursery directories for Oregon and Washington (links below) to find nurseries that carry this species.
What growing conditions does Sitka Spruce need?
See the Growing & Care Guide section above for detailed light, soil, and water requirements specific to this species.
![]()
Looking for a nursery that carries Sitka Spruce?
Browse our native plant nursery directory: Oregon · Washington